ZNA® (Figure 1) stands for Zip Nucleic Acid, which consist in oligonucleotides conjugated with cationic spermine units. This asset decreases the electrostatic repulsion between single strand nucleic acids (i.e. between primer/probe and target DNA during annealing). As a result, ZNA® primers and probes have higher affinity to their targets, compared to unmodified oligonucleotides. Moreover, the global charge of a ZNA® oligonucleotide-oligocation can be modulated by specifying the number of cationic spermine moieties attached to the nucleic acid oligomer. The Tm of ZNAs® increases linearly with the length of the oligocation. Therefore, it is possible to easily predict the melting temperature (Tm) of ZNA®-DNA or ZNA®-RNA hybrids.
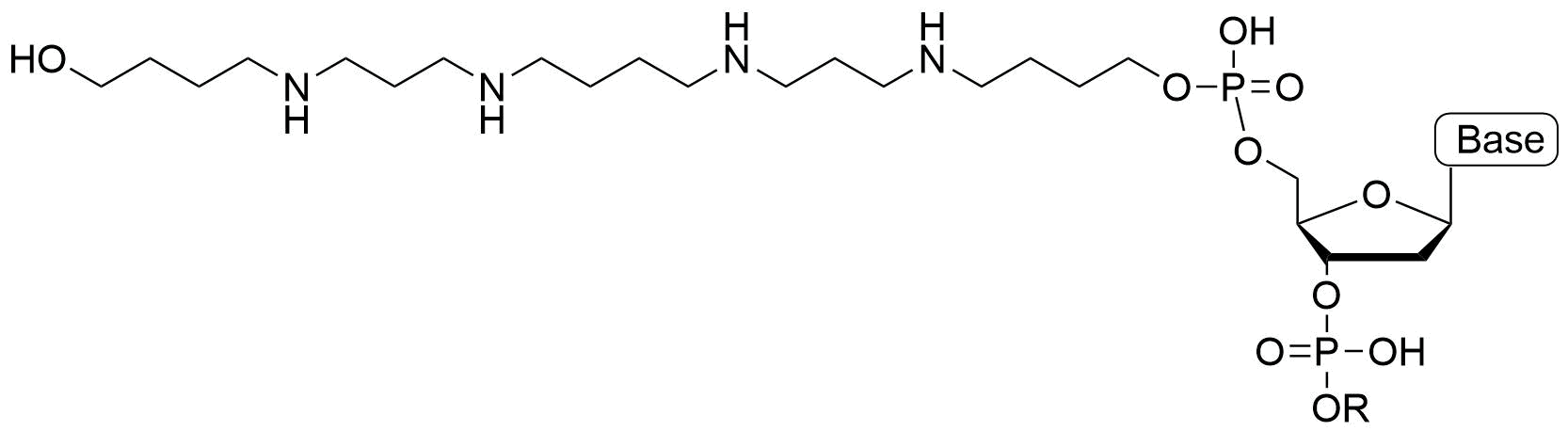
Figure 1. Structure of one single 5'-ZNA (R = sequence).
metabion offers ZNA® modifications in its DNA portfolio:
For more information, please visit our Portfolio. To place an order, click here.
References
- Paris C., Moreau V., Deglane G., Voirin E., Erbacher P., Lenne-Samuel N. Zip nucleic acids are potent hydrolysis probes for quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Apr;38(7):e95.
- Moreau V., Voirin E., Paris C., Kotera M., Nothisen M., Rémy JS., Behr JP., Erbacher P., Lenne-Samuel N. Zip Nucleic Acids: new high affinity oligonucleotides as potent primers for PCR and reverse transcription. Nucleic Acids Res.
2009 Oct;37(19):e130.
- Noir R., Kotera M., Pons B., Remy JS., Behr JP. Oligonucleotide-oligospermine conjugates (zip nucleic acids): a convenient means of finely tuning hybridization temperatures. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Oct 8;130(40):13500-5.

